Hydraulic systems sit at the core of every ISUZU dump truck, quietly transforming engine power into controlled lifting force that enables efficient material handling on construction sites, municipal projects, and industrial operations. While these systems are designed for durability, their real-world reliability depends heavily on disciplined maintenance, informed inspection routines, and an operator’s understanding of how hydraulic components interact under load and pressure. Poor hydraulic maintenance rarely fails suddenly; instead, it reveals itself gradually through slower lifting speeds, unstable dumping actions, increased oil temperatures, and premature component wear. By adopting a structured approach to hydraulic system care, operators and fleet managers can significantly extend service life, reduce downtime, and protect the overall value of their ISUZU dump trucks.
Understanding the Hydraulic System Architecture in ISUZU Dump Trucks
A strong maintenance strategy begins with a clear understanding of how the hydraulic system is structured and how each component contributes to overall functionality.
Core Components and Functional Roles
The hydraulic system in an ISUZU dump truck typically consists of a hydraulic pump, control valves, hydraulic cylinders, oil reservoir, filters, hoses, and fittings, all working together as a pressurized closed-loop system. The pump converts mechanical energy into hydraulic flow, the valves regulate direction and pressure, and the cylinders translate fluid power into linear lifting motion. Each component is engineered to precise tolerances, meaning that contamination, pressure imbalance, or improper lubrication in one area can affect the entire system.
Pressure, Flow, and Load Relationships
Hydraulic performance is governed by the balance between pressure and flow rate, both of which are directly influenced by load conditions. Excessive load forces the system to operate at higher pressures, increasing heat generation and accelerating seal wear. Understanding these relationships helps operators avoid practices that push the system beyond its optimal operating range, reinforcing the idea that maintenance is as much about proper usage as it is about scheduled servicing.

Hydraulic Oil Management as the Foundation of System Health
Among all maintenance tasks, hydraulic oil management has the most profound impact on long-term system reliability, yet it is often underestimated in daily operations.
Selecting the Correct Hydraulic Oil
ISUZU specifies hydraulic oils with carefully balanced viscosity characteristics that ensure proper flow across a wide temperature range. Using oil with incorrect viscosity can lead to sluggish operation in cold conditions or excessive internal leakage at high temperatures. Sticking to manufacturer-recommended oil grades preserves pump efficiency, protects seals, and stabilizes system pressure under varying workloads.
Oil Cleanliness and Contamination Control
Hydraulic oil is not merely a lubricant; it is also a power transmission medium, which makes cleanliness absolutely critical. Dust, metal particles, and moisture introduced during oil changes or through damaged seals act as abrasives that erode internal surfaces over time. Regular oil sampling and visual inspection help identify contamination early, while disciplined refilling procedures prevent unnecessary exposure to airborne particles.
Inspection and Maintenance of Hydraulic Hoses, Seals, and Fittings
While major components often receive attention, minor elements such as hoses and seals frequently determine whether a hydraulic system remains reliable or becomes a recurring source of failure.
Hose Integrity and Routing
Hydraulic hoses operate under constant pressure cycles and are exposed to vibration, heat, and environmental hazards. Routine inspection for surface cracks, bulging, abrasion, or oil seepage allows early replacement before catastrophic rupture occurs. Proper routing and secure clamping prevent hoses from rubbing against sharp edges or hot exhaust components, preserving both safety and system efficiency.
Seal Condition and Leakage Prevention
Seals within cylinders and valves maintain pressure integrity, yet they naturally degrade over time due to heat and mechanical stress. Small leaks around cylinder rods or valve bodies should never be ignored, as they indicate internal wear that can escalate quickly. Addressing seal issues early minimizes oil loss, prevents contamination ingress, and avoids secondary damage to pumps and control valves.
Hydraulic Cylinder Care and Dumping Mechanism Stability
The hydraulic cylinder is the visible workhorse of the dump truck, and its condition directly affects lifting smoothness, load stability, and operational safety.
Surface Protection and Rod Maintenance
Cylinder rods must remain clean and free from scoring to maintain seal effectiveness. Dirt accumulation or corrosion on exposed rod surfaces accelerates seal wear during extension and retraction cycles. Regular cleaning after operation, especially in muddy or corrosive environments, significantly extends cylinder service life.
Alignment and Load Distribution
Uneven loading within the dump body introduces side loads on hydraulic cylinders, increasing stress on mounting points and internal components. Operators should ensure that materials are distributed evenly and that dumping is performed on stable, level ground whenever possible. Maintaining proper alignment not only protects the cylinder but also preserves chassis integrity and tipping stability.
Monitoring Hydraulic System Performance During Daily Operations
Maintenance does not occur solely in workshops; attentive observation during daily operation often reveals early warning signs that scheduled inspections might miss.
Recognizing Early Performance Changes
Slower lift times, inconsistent dumping speed, unusual noises from the pump, or elevated oil temperatures are all indicators of developing issues. Treating these symptoms as actionable maintenance signals rather than tolerable inconveniences allows problems to be addressed before they escalate into costly failures.
Operator Training and Awareness
Well-trained operators play a crucial role in hydraulic system longevity. Avoiding abrupt control inputs, allowing adequate warm-up time in cold conditions, and respecting load limits all reduce stress on hydraulic components. Embedding hydraulic awareness into operator training programs transforms maintenance from a reactive process into a proactive culture.
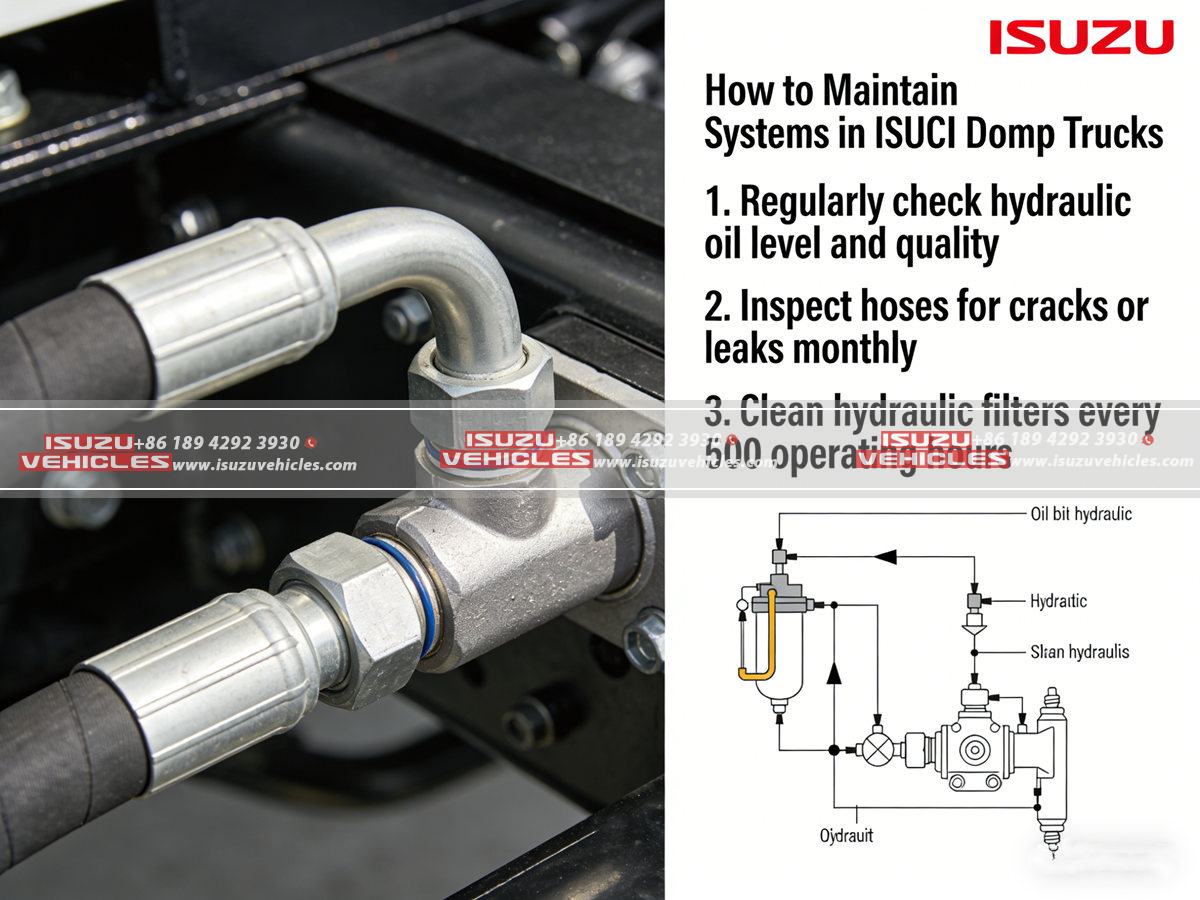
Long-Term Maintenance Planning and Fleet-Level Best Practices
Hydraulic system care yields the greatest benefits when it is integrated into a structured, long-term maintenance framework rather than treated as isolated tasks.
Scheduled Servicing and Record Keeping
Establishing consistent maintenance intervals for oil changes, filter replacement, and component inspection creates predictable performance and budgeting stability. Detailed service records help identify recurring issues and inform decisions about component upgrades or operational adjustments.
Application-Specific Adaptation
Different work environments impose unique demands on hydraulic systems. Urban construction, mining, and municipal waste handling each introduce distinct contamination risks and duty cycles. Adapting maintenance practices to real-world operating conditions ensures that ISUZU dump trucks deliver reliable performance regardless of application.
In modern mixed fleets, hydraulic maintenance principles developed for dump trucks often carry over to other specialized vehicles, reinforcing system-wide reliability standards. Whether managing lifting mechanisms on an ISUZU box truck configured for specialized cargo handling or overseeing high-duty-cycle equipment such as an ISUZU mixer truck, the same disciplined approach to oil cleanliness, component inspection, and operator awareness proves invaluable. By treating hydraulic systems as precision assemblies rather than simple mechanical tools, operators ensure that ISUZU vehicles continue to deliver controlled power, operational safety, and dependable performance across diverse working environments.
