In modern logistics, energy consumption represents a substantial portion of operational costs, particularly for temperature-controlled transport such as ISUZU reefer trucks. These vehicles are tasked with maintaining precise refrigeration conditions over extended routes, often under variable ambient temperatures, traffic conditions, and cargo loads. While ISUZU designs its refrigerated trucks for optimized thermal performance and fuel efficiency, achieving meaningful reductions in energy usage depends heavily on operator awareness, disciplined maintenance practices, and intelligent operational planning. Reducing energy consumption not only lowers costs but also minimizes environmental impact, contributing to more sustainable supply chain practices across industries.
Understanding Energy Dynamics in Reefer Trucks
To effectively reduce energy consumption, it is essential first to understand how power is utilized within a reefer truck, and how various systems interact to maintain operational performance.
Engine Load and Refrigeration Demand
The refrigeration unit in a reefer truck relies on the engine or an auxiliary power source to drive compressors and maintain temperature stability. Higher ambient temperatures, frequent door openings, and heavy cargo loads increase compressor workload, which in turn increases fuel or electricity consumption. Understanding this relationship allows operators to identify opportunities to reduce unnecessary energy expenditure, such as minimizing door openings or optimizing route planning to reduce idle time in high-temperature conditions.
Thermal Efficiency and Insulation Impact
Thermal losses represent a hidden but significant contributor to energy use. Inadequate insulation, damaged seals, or poor body maintenance forces refrigeration systems to work harder to compensate for heat gain. Ensuring that insulation materials, gaskets, and door seals remain in optimal condition is fundamental to energy conservation. This principle is particularly relevant for ISUZU reefer trucks, which are designed with highly efficient insulation but rely on proper upkeep to maintain peak thermal performance over years of operation.
Optimizing Driving Habits for Fuel Efficiency
Operator behavior is one of the most influential and often overlooked factors affecting energy consumption in reefer trucks. Small adjustments in driving technique can result in significant savings over the long term.
Smooth Acceleration and Deceleration
Aggressive acceleration and frequent hard braking increase engine load and, indirectly, refrigeration energy demand. By encouraging smooth throttle application and anticipating traffic conditions, drivers can maintain a more consistent engine speed, reducing overall fuel consumption. Additionally, stable speed profiles help the refrigeration system operate efficiently, as fluctuating engine output can disrupt compressor performance.
Strategic Idling and Auxiliary Power Use
Many operators rely on idling to maintain temperature control while stationary, but excessive idling wastes fuel and increases emissions. Where possible, using insulated covers for doors, parking in shaded areas, or deploying auxiliary power units specifically designed for refrigeration can reduce the engine’s energy load. Properly monitoring idle duration and using automatic shutdown features helps align engine operation with refrigeration needs, preventing unnecessary energy loss.
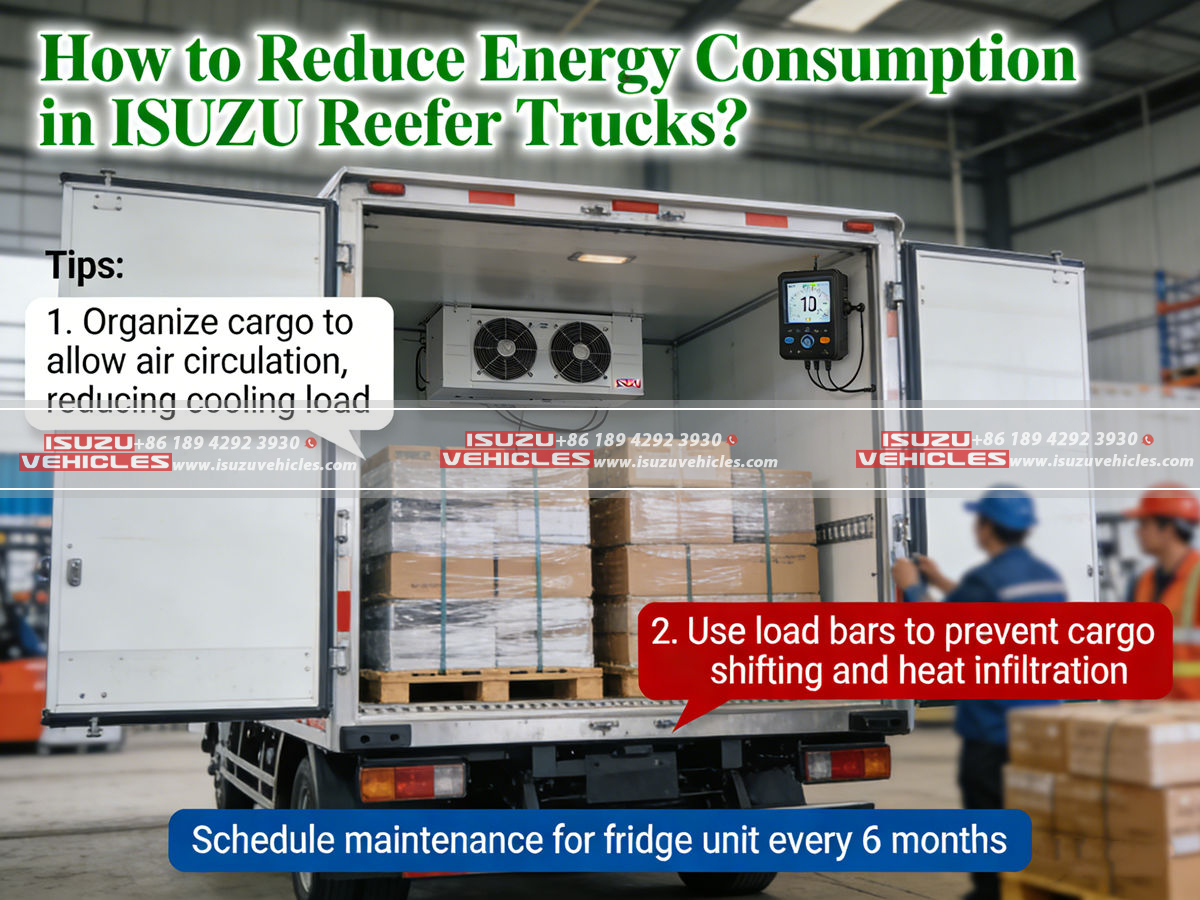
Maintaining Refrigeration Systems for Optimal Efficiency
The refrigeration unit itself represents the primary energy consumer in a reefer truck, and its efficiency is heavily dependent on proper maintenance and calibration.
Regular Service and Component Inspection
Routine checks of compressors, condensers, evaporators, and fans prevent mechanical inefficiencies that increase energy consumption. Debris accumulation, damaged components, or refrigerant leaks force the system to operate longer or at higher intensity, directly raising fuel usage. Implementing a structured maintenance schedule, including pre-trip inspections, ensures that the refrigeration unit consistently performs at designed efficiency levels.
Refrigerant Management and System Tuning
Refrigerant type, charge level, and system calibration significantly affect energy efficiency. Low refrigerant levels or improper pressure settings reduce cooling efficiency, causing the compressor to work harder. Following manufacturer guidelines for refrigerant replacement, system flushing, and pressure checks ensures that the unit maintains optimal thermal transfer, minimizing unnecessary energy expenditure.
Aerodynamics and Body Maintenance for Reduced Consumption
The truck’s body design and condition influence both driving fuel efficiency and refrigeration energy requirements, particularly on long-distance routes.
Streamlined Load Profiles
Excess cargo protrusions, poorly secured tarpaulins, or irregular load distribution increase aerodynamic drag, requiring higher engine output to maintain speed. This additional load indirectly increases refrigeration energy consumption, as engine-driven compressors work harder under higher torque conditions. Maintaining clean, uniform load profiles and using aerodynamic aids where appropriate can reduce overall energy demands.
Seal Integrity and Door Maintenance
The interface between the cargo space and external environment is critical in thermal efficiency. Worn door seals, misaligned panels, or gaps around insulation can allow warm air infiltration, forcing the refrigeration unit to operate at higher intensity. Routine inspection of doors, gaskets, and hinges preserves both thermal containment and energy efficiency, ensuring that refrigeration demand aligns with design specifications.

Route Planning and Operational Scheduling
Intelligent planning is a practical yet highly effective method for reducing energy consumption in ISUZU reefer trucks.
Minimizing Stop-and-Go Traffic
Frequent stops and prolonged congestion increase engine load, elevate fuel consumption, and disrupt stable refrigeration operation. Planning routes that avoid peak congestion periods, construction zones, or inefficient detours allows trucks to maintain steady speed, which benefits both the engine and refrigeration system. Additionally, scheduling deliveries during cooler periods of the day reduces thermal stress on the unit, lowering energy usage.
Load Consolidation and Delivery Sequencing
Efficient route sequencing ensures that trucks carry the maximum feasible load without exceeding weight or thermal limits, reducing the number of trips required to complete deliveries. Consolidated loads minimize engine operation hours and refrigeration cycles, directly translating into lower energy consumption. Proper sequencing also reduces door openings at each stop, preserving internal temperature and reducing compressor runtime.
Integrating Technology and Fleet-Wide Energy Management
Modern reefer fleets benefit from technology integration, which allows operators to monitor, adjust, and optimize energy consumption on a continuous basis.
Telematics and Fuel Monitoring Systems
Telematics systems track engine performance, fuel usage, refrigeration cycles, and temperature consistency, providing actionable insights into operational efficiency. By analyzing this data, fleet managers can identify patterns of excessive energy use, implement targeted training programs, and adjust operational parameters to optimize consumption across the entire fleet.
Hybrid Solutions and Auxiliary Power Units
Emerging solutions such as hybrid drive systems, electric auxiliary refrigeration units, and regenerative braking technologies further enhance energy efficiency. Incorporating these systems allows ISUZU reefer trucks to maintain cooling performance while reducing dependency on traditional engine power, particularly in urban stop-and-go operations.
By combining disciplined driving behavior, structured maintenance, aerodynamic care, intelligent routing, and modern energy management technologies, operators can achieve measurable reductions in energy consumption while preserving cargo integrity and vehicle performance. These principles apply across multiple ISUZU platforms, from versatile ISUZU box truck models used in local distribution to heavier ISUZU cargo truck configurations deployed on regional refrigerated transport routes, demonstrating that energy-conscious operations are both economically and environmentally advantageous.
